File:Dram-abs.jpg
Size of this preview: 800 × 432 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 173 pixels | 640 × 346 pixels | 1,024 × 553 pixels | 1,641 × 886 pixels.
Original file (1,641 × 886 pixels, file size: 183 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
File information
Structured data
Captions
Captions
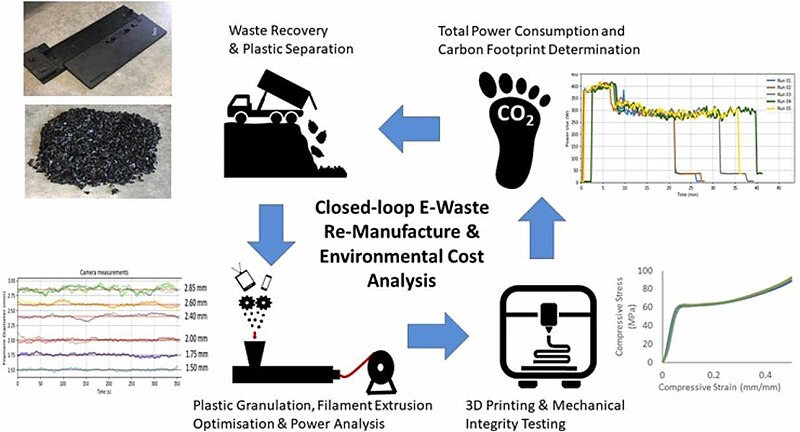
Sustainability and Feasibility Assessment of Distributed E-Waste Recycling using Additive Manufacturing in a Bi-Continental Context
Summary edit
| DescriptionDram-abs.jpg |
English: The most abundant e-waste plastic is acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), which is not typically processed by municipal programs and is equally one of the most popular 3-D printing filaments. This makes ABS a prime candidate for the distributed recycling for additive manufacturing (DRAM) approach, which has the potential to increase recycling rates by providing economic incentive for consumers to recycle. For DRAM to be globally applicable, this study investigates the role of the ABS e-waste source and processes to fabricate 3-D printing filament and printed components in both Australia and North America. The study used two different open source extruder systems to convert e-waste into 3D printer filament and for material quality to be assessed through standardized tensile and compression testing. Results revealed a modest reduction in mechanical properties compared to virgin ABS, highlighting the potential for recycled e-waste ABS for consumer and industrial uses. We also show DRAM can significantly reduce 3-D printer filament cost, however, carbon emissions from conversion underscored the need for technical efficiency improvements in electricity generating between countries. Finally, the variations in the properties of the ABS e-waste indicates the need for appropriate labeling of materials in order to advance recycling.
Mazher Mohammed, Daniel Wilson, Eli Gomez-Kervin, Aliaksei Petsiuk, Rachel Dick, Joshua M. Pearce. Sustainability and Feasibility Assessment of Distributed E-Waste Recycling using Additive Manufacturing in a Bi-Continental Context. Additive Manufacturing. 50, 102548 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2021.102548, academia. |
| Date | |
| Source | https://www.appropedia.org/Sustainability_and_Feasibility_Assessment_of_Distributed_E-Waste_Recycling_using_Additive_Manufacturing_in_a_Bi-Continental_Context |
| Author | Joshua M. Pearce |
Licensing edit
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license.
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- share alike – If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same or compatible license as the original.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 20:05, 18 November 2023 |  | 1,641 × 886 (183 KB) | Yew know (talk | contribs) | Uploaded a work by Joshua M. Pearce from https://www.appropedia.org/Sustainability_and_Feasibility_Assessment_of_Distributed_E-Waste_Recycling_using_Additive_Manufacturing_in_a_Bi-Continental_Context with UploadWizard |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage on Commons
The following page uses this file:
Metadata
This file contains additional information such as Exif metadata which may have been added by the digital camera, scanner, or software program used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details such as the timestamp may not fully reflect those of the original file. The timestamp is only as accurate as the clock in the camera, and it may be completely wrong.
| JPEG file comment | HiRes |
|---|