File:XRT schematic.jpg
XRT_schematic.jpg (514 × 331 pixels, file size: 38 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Captions
Captions
Summary edit
| DescriptionXRT schematic.jpg |
English: The layout of the XRT is shown in the schematic. Swift's X-Ray Telescope (XRT) is designed to measure the fluxes, spectra, and lightcurves of GRBs and afterglows over a wide dynamic range covering more than 7 orders of magnitude in flux. The XRT can pinpoint GRBs to 5-arcsec accuracy within 10 seconds of target acquisition for a typical GRB and can study the X-ray counterparts of GRBs beginning 20-70 seconds from burst discovery and continuing for days to weeks. |
| Date | |
| Source | Swift: Catching Gamm-Ray Bursts on the Fly. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center |
| Author | Swift PI: Neil Gehrels, Responsible NASA Official: Phil Newman Web Curator: J.D. Myers PAO Contact: Francis Reddy |
| Permission (Reusing this file) |
Images produced by NASA are usually free of copyright [...] |
The XRT is a focusing X-ray telescope with a 110 cm2 effective area, 23.6 x 23.6 arcmin FOV, 18 arcsec resolution (half-power diameter), and 0.2-10 keV energy range. The XRT uses a grazing incidence Wolter 1 telescope to focus X-rays onto a state-of-the-art CCD. The complete mirror module for the XRT consists of the X-ray mirrors, thermal baffle, a mirror collar, and an electron deflector. The X-ray mirrors (left) are the FM3 units built, qualified and calibrated as flight spares for the JET-X instrument on the Spectrum X-Gamma mission (Citterio et al. 1996; Wells et al. 1992; Wells et al. 1997). To prevent on-orbit degradation of the mirror module's performance, it is be maintained at 20 +/- 5 degrees C, with gradients of <1 degree C by an actively controlled thermal baffle (purple, in schematic below) similar to the one used for JET-X. A composite telescope tube holds the focal plane camera (red), containing a single CCD-22 detector. The CCD-22 detector, designed for the EPIC MOS instruments on the XMM-Newton mission, is a three-phase frame-transfer device, using high resistivity silicon and an open-electrode structure (Holland et al. 1996) to achieve a useful bandpass of 0.2-10 keV (Short, Keay, & Turner 1998).
Licensing edit
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
| This file is in the public domain in the United States because it was solely created by NASA. NASA copyright policy states that "NASA material is not protected by copyright unless noted". (See Template:PD-USGov, NASA copyright policy page or JPL Image Use Policy.) |  | |
 |
Warnings:
|
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 01:04, 12 September 2009 | 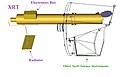 | 514 × 331 (38 KB) | Marshallsumter (talk | contribs) | {{Information |Description={{en|1=The layout of the XRT is shown in the schematic. Swift's X-Ray Telescope (XRT) is designed to measure the fluxes, spectra, and lightcurves of GRBs and afterglows over a wide dynamic range covering more than 7 orders of ma |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage on Commons
There are no pages that use this file.
File usage on other wikis
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on az.wikipedia.org
- Usage on ru.wikipedia.org
- Usage on tr.wikipedia.org
Metadata
This file contains additional information such as Exif metadata which may have been added by the digital camera, scanner, or software program used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details such as the timestamp may not fully reflect those of the original file. The timestamp is only as accurate as the clock in the camera, and it may be completely wrong.
| _error | 0 |
|---|
