Category:3-ary Boolean functions; cube permutations
| permuting 3 arguments | |
|---|---|

|

|
| original order or arguments |
|---|

|
| permuting 2 arguments | ||
|---|---|---|

|

|

|


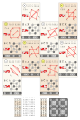
Permutations of a cube (or a vector of length 8) corresponding to 3-ary Boolean functions in a big equivalence class (compare this category)
The 48 permutations are the elements of the full octahedral group (FOG).
The 8×6 matrix on the right shows that each of these permutations can be written as .
Each file corresponds to a permutation of the 3 arguments - and to a column of that matrix.
SVG files edit
The data shown in these images can be found in here.
The SVG files have been created with Python using this script and these templates.
The permutations (maps from to itself) are shown in the upper half of each rectangle and on the left in the footer of each file.
The results of applying them to the sequence are shown in the lower half of each rectangle and on the right in the footer.
The results are always shown with a gray background. (Dark gray for numbers with odd binary digit sum.)
All the gray 8×8 matrices have the pattern of the XOR table in file 0. So replacing a set of numbers with 1s and the others with 0s gives a SEC matrix.
Mathematical description edit
Let be a 3-ary Boolean function, a negator pattern and a permutation of 3 elements.
Then the truth table of with and then the inverse of applied to its arguments
is the initial truth table permuted by :
(Some parentheses omitted for readability.)
Finding the position edit
The position of among the 48 permutations is to be found.
(Compare Permutation notation)
So is at position ![]() in cube
in cube ![]() , and its truth table is that of permuted by .
, and its truth table is that of permuted by .
(Compare File:Cube permutation 4 3.svg)
For the sake of simplicity the truth table of the initial function is identified () with the integers 0..7:
(As usual when dealing with permutations that are not self-inverse, there is the danger of confusing a permutation with the result of applying it to the natural order.
That is why both the permutations and their results are shown in these graphics.)
Specific Boolean function edit
![]() .
It is at position
.
It is at position ![]() in this cube (
in this cube (![]() with unrotated functions).
with unrotated functions).
![]() .
It is at position
.
It is at position ![]() in this cube (
in this cube (![]() with rotations to the left).
with rotations to the left).
While the positions of general formulas like or are unique, for specific there is always at least one duplicate,
because the maximum number of functions in a big equivalence class (of 3-ary Boolean functions) is 24.
For the in the above example and .
That means that and have no effect and and have the same effect on the truth table of .
Compare File:Hyperoctahedral group 2; active postfix.svg with permutations of a square
Media in category "3-ary Boolean functions; cube permutations"
The following 6 files are in this category, out of 6 total.
-
3-ary Boolean functions; cube permutations; 0.svg 860 × 1,282; 74 KB
-
3-ary Boolean functions; cube permutations; 1.svg 860 × 1,282; 75 KB
-
3-ary Boolean functions; cube permutations; 2.svg 860 × 1,282; 75 KB
-
3-ary Boolean functions; cube permutations; 3.svg 860 × 1,282; 76 KB
-
3-ary Boolean functions; cube permutations; 4.svg 860 × 1,282; 76 KB
-
3-ary Boolean functions; cube permutations; 5.svg 860 × 1,282; 75 KB